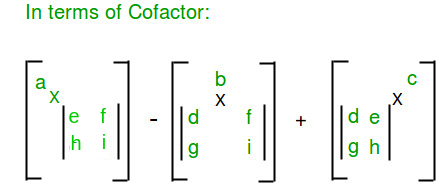
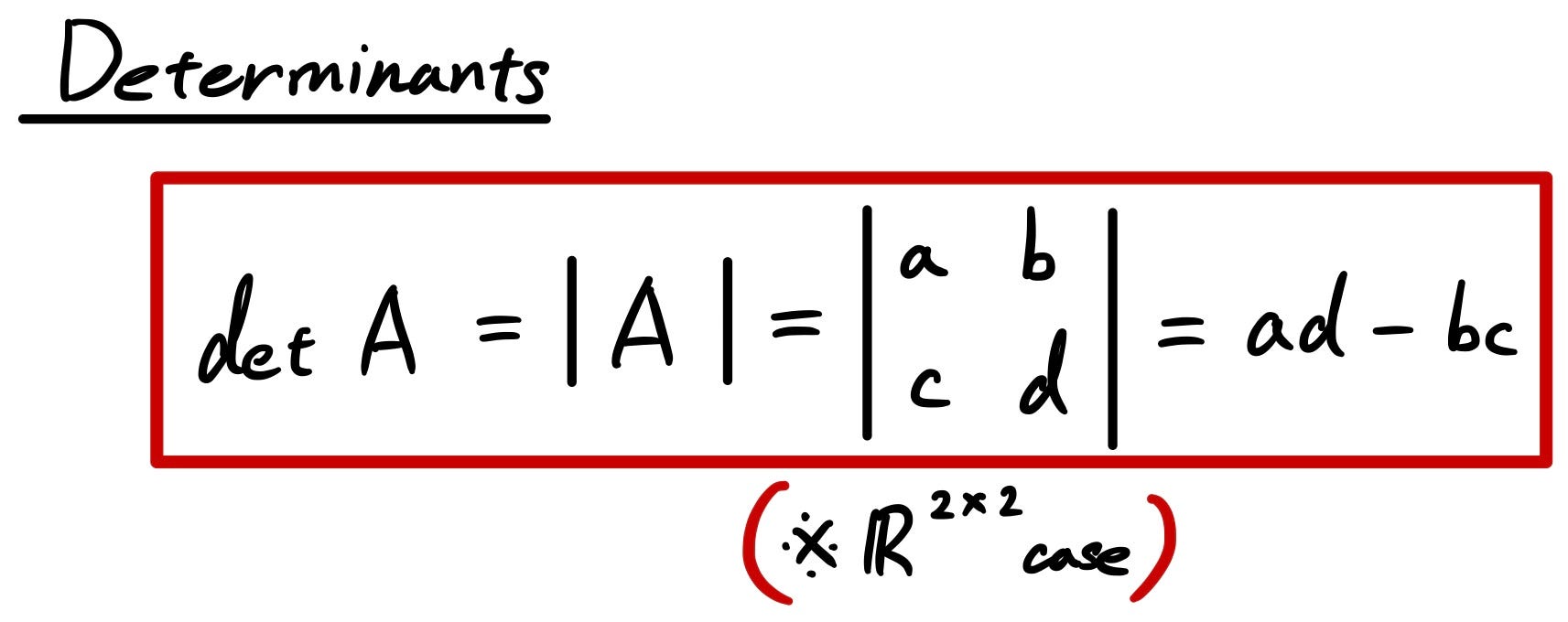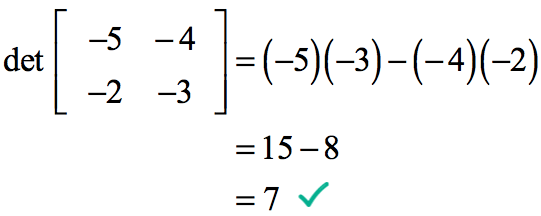Determinants can be used to solve linear systems using cramer s rule where the division of the determinants of two related square matrices equates to the value of each of the system s variables.
What is a matrix determinant used for.
I find this interpretation to be the most intuitive and many standard results for determinants can be understood using this viewpoint.
The determinant of a matrix.
To understand determinant calculation better input any example choose very detailed solution option and examine the solution.
A matrix is an array of many numbers.
You can know a few things with it.
The determinant helps us find the inverse of a matrix tells us things about the matrix that are useful in systems of linear equations calculus and more.
For example a matrix is often used to represent the coefficientsin a system of linear equations and the determinant can be used to solvethose equations although other methods of solution are much more computationally efficient.
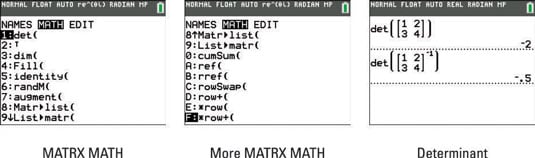
The determinant of a matrix a helps you to find the inverse matrix a 1.
However i have rarely had a practical need to compute volumes using determinants.
A is invertible if and only if det a 0.
The most obvious use you may find is indirect within broader procedures like the degree of a non square matrix linear in dependence linear systems and so on.
For a square matrix i e a matrix with the same number of rows and columns one can capture important information about the matrix in a just single number called the determinant.
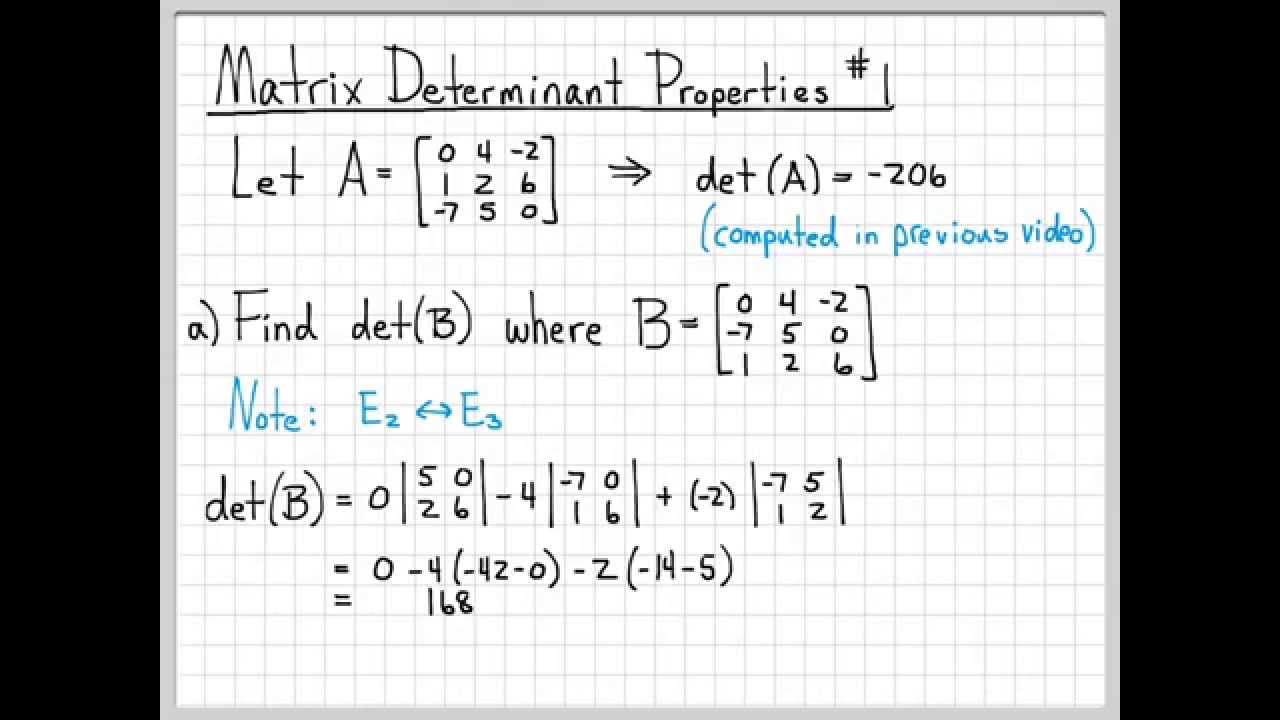
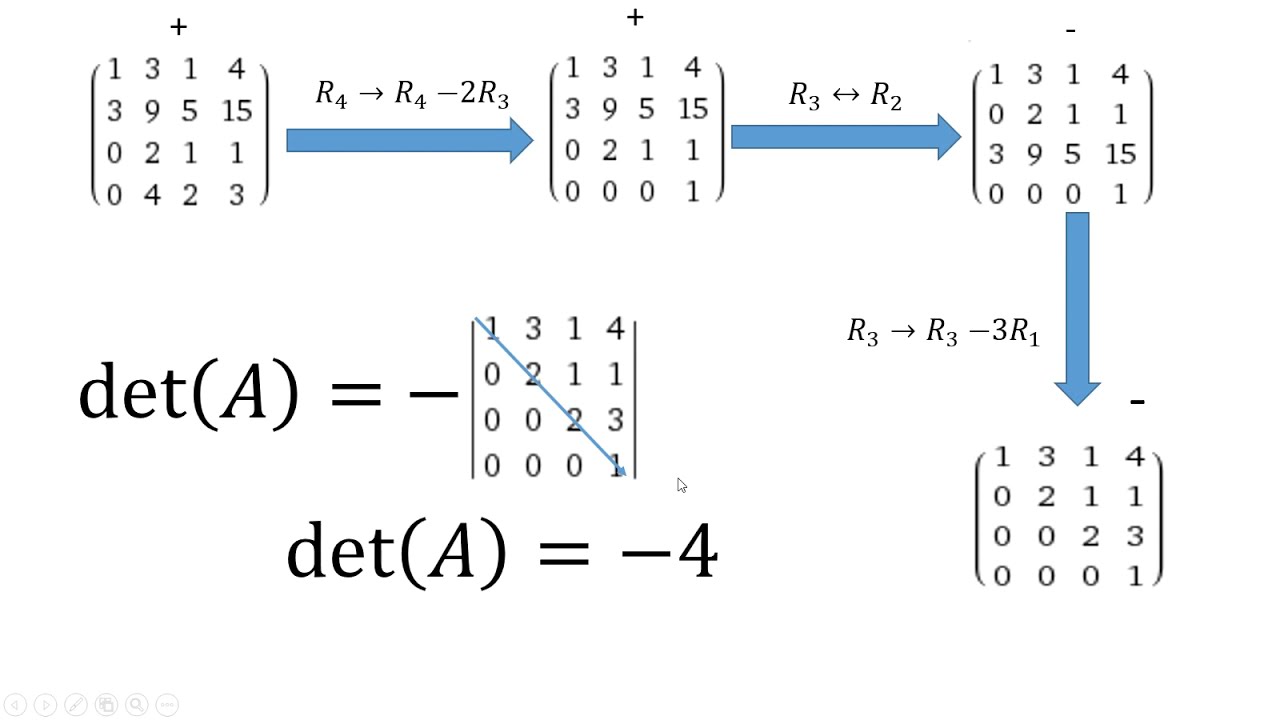
Reduce this matrix to row echelon form using elementary row operations so that all the elements below diagonal are zero.
The determinant is useful for solving linear equations capturing how linear transformation change area or volume and changing variables in integrals.
The determinant also gives the signed volume of the parallelepiped whose edges are the rows or columns of a matrix.
Multiply the main diagonal elements of the matrix determinant is calculated.
The determinant of a matrix gives information about how the associated linear transformation changes the area volume of a unit square cube hypercube.
Determinants occur throughout mathematics.
Det a 1 1 det a.