However chemical and physical weathering often go hand in hand.
What climate affects chemical weathering of granite.
Chemical weathering alters the composition of the rock material toward surface minerals such as clays.
Chemical reactions proceed more rapidly at higher temperatures.
List the products of chemical weathering of each of the minerals in each of these rocks.
Limestone areas are predominantly affected by chemical weathering when rainwater which contains a weak carbonic acid reacts with limestone.
Chemical weathering increases as.
Weathering therefore occurs more slowly in granite than in layered sedimentary rocks.
It results from the reaction of aqueous acidic and oxidizing solutions with the minerals in rocks and soils.
Chemical weathering of rocks is a spontaneous i e irreversible thermodynamic process leading to a more stable state for natural materials under a given set of conditions e g temperature and pressure.
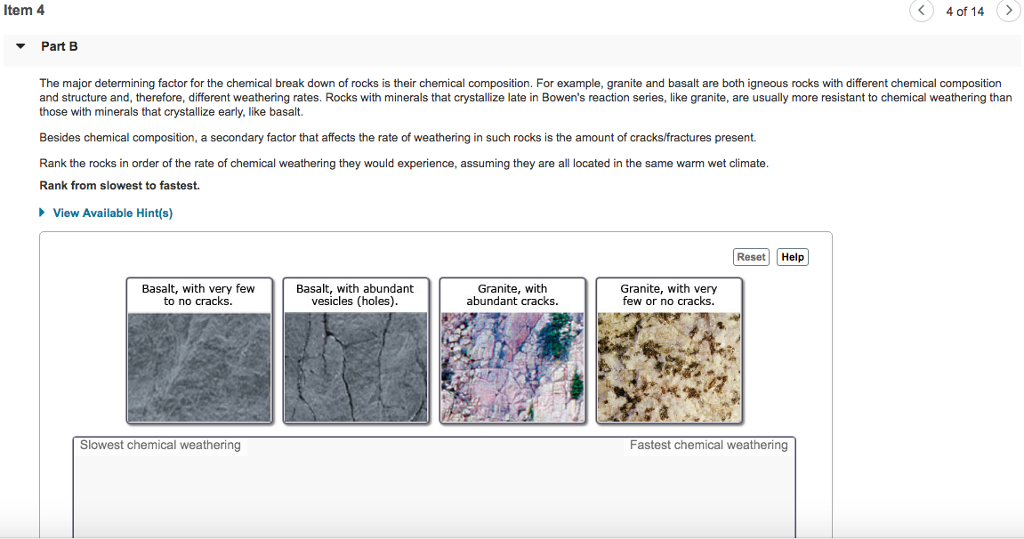
Besides chemical composition a secondary factor that affects the rate of weathering in such rocks is the amount of cracks fractures present.
Climate is determined by the temperature of a region plus the amount of precipitation it receives.
A region s climate strongly influences weathering.
Carbon dioxide from the respiration of animals and ourselves is one cause of increased carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
High temperatures and greater rainfall increase the rate of chemical weathering.
Weathering is the breakdown of rock by physical chemical or biological processes.
This causes the limestone to dissolve.
Draw a conclusion as to which rock type is more resistant to weathering in a humid climate.
Rank the rocks in order of the rate of chemical weathering they would experience assuming they are all located in the same warm wet climate.
Climate influences weathering over short and longer periods of time.
Climate is weather averaged over a long period of time.
Observe and measure the effects of chemical weathering and mechanical weathering in a humid climate on headstones of granite and marble each of different ages.
Rank from slowest to fastest.
Physical weathering also called mechanical weathering or disaggregation is the class of processes that causes the disintegration of rocks without chemical change the primary process in physical weathering is abrasion the process by which clasts and other particles are reduced in size.
Granite is extremely hard and less affected by the freeze thaw cycle the forces of abrasion and the surface exfoliation processes that are all a part of physical weathering.
It attacks minerals that are relatively unstable in surface conditions such as the primary minerals of igneous rocks like basalt granite or peridotite.
A gravestone made of granite will therefore resist fracturing cracking and chipping longer than a sandstone marker found in the same location.