Wharton s jelly derived mesenchymal stem cells wj mscs have a high proliferation valency and they do not produce teratogen or carcinogen after subsequent transplantation.
Wharton s jelly derived mesenchymal stem cells.
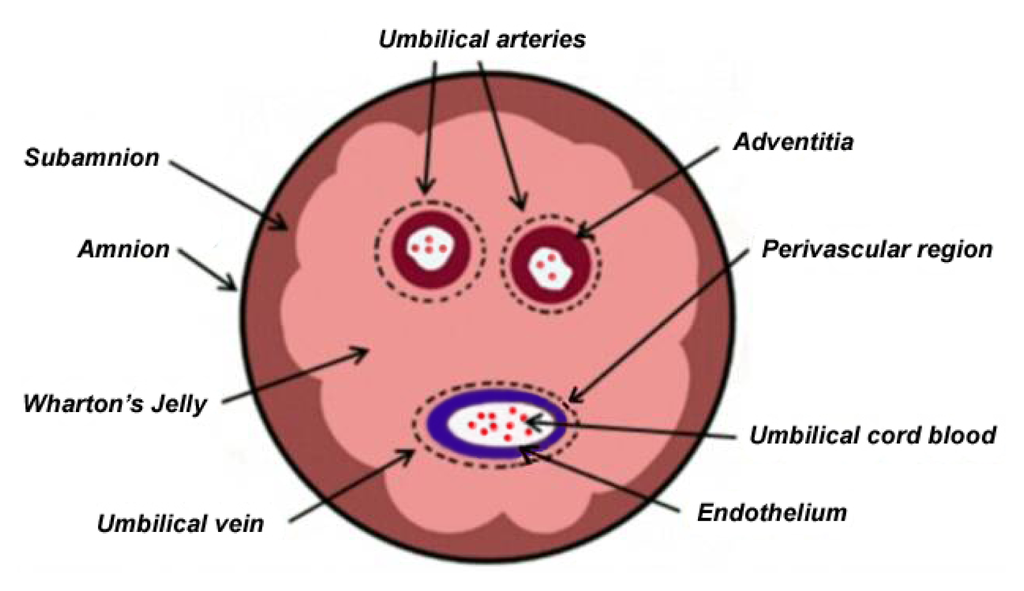
Wharton s jelly is therefore a potential source of adult stem cells often collected from cord blood.
Evidences that these cells possess therapeutic properties are constantly accumulating.
Wharton s jelly mesenchymal stromal stem cells are harvested from umbilical cord tissue and are considered by many regenerative experts to have the most potential for effective cell based therapy with the added benefit of being far easier and less invasive to retrieve.
Wharton s jelly derived mesenchymal stem cells may have immunomodulatory effect on lymphocytes.
This cord prevents umbilical vessels from kinking compression or torsion during movement of the fetus thus ensuring proper blood supply to the fetus kim et al 2013.
Around 5 million annual births in eu and 131 million worldwide give a unique opportunity to collect lifesaving wharton s jelly derived mesenchymal stem cells wj msc.
The aim of this study was to investigate the possibility of using human wharton s jelly derived mesenchymal stem cells msc s for lung recovery in a copd mouse model.
Additional benefits of wharton s jelly mscs.
In a recent study wharton s jelly tissue transplantation has shown to be able to reduce traumatic brain injury and may have therapeutic potential.
They are known as regenerative medicine.
Evidences that these cells possess therapeutic properties are constantly accumulating.
Wharton s jelly derived stem cells on the other hand appear to circumvent both of these problems making them valuable for a variety of applications in medicine.
Thus more research is needed on the isolation and characterization of mesenchymal stem cells.
Collection of wj msc is done at the time of delivery and it is easy and devoid of side effects associated with collection of adult stem.
Mesenchymal stem cells which are the basis for a number of stem cell therapies and the relevant research may be limited in value when they have been collected from older patients.
The connective tissue of the human umbilical cord wharton s jelly is garnering increasing attention as a source of mesenchymal stromal cells and is now being employed in clinical trials.